Introduction: The Challenge of Ever-Evolving Medical Knowledge
Medical knowledge is a dynamic field, continuously shaped by discoveries, evolving treatment modalities, and changing healthcare policies. Professionals must adapt to stay current, integrating breakthroughs in genomics, immunotherapy, and precision medicine into their practice. Traditional methods like textbooks and clinical rotations are foundational but may struggle to keep pace with the rapid evolution of medical knowledge.
However, emerging technologies offer opportunities to enhance traditional learning approaches. Large language models (LLMs) and generative AI provide interactive, personalized learning experiences by processing extensive medical literature and simulating clinical scenarios. These innovative tools supplement traditional methods, equipping medical professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to provide optimal patient care in today’s dynamic healthcare landscape.
The Potential of Large Language Models in Medical Education

Large language models (LLMs) and generative AI have revolutionized natural language processing, enabling the generation of human-like text based on vast datasets. With training in diverse domains, including medicine, LLMs like GPT-3 and GPT-4 possess the ability to mimic human language comprehension effectively. In medical education, LLMs offer unparalleled potential to process complex literature, simulate clinical scenarios, and provide personalized learning experiences for professionals.
LLMs can be harnessed to explain medical concepts, simulate patient interactions, and generate assessments, enhancing both comprehension and practical skills. Through interactive applications, educators can create dynamic learning environments tailored to individual needs. By integrating LLMs into medical education, professionals gain access to innovative tools that bridge traditional learning methods with cutting-edge technology, fostering continuous growth and adaptation in the ever-evolving field of medicine.
Interactive Learning with LLMs: Beyond Traditional Methods

Traditional methods of medical education often rely on passive learning techniques such as lectures, textbooks, and written examinations. While these methods are valuable, they may not always effectively engage learners or address their individual learning needs. In contrast, LLMs offer a novel approach to education by providing interactive and personalized learning experiences that go beyond traditional methods. Here is a comparison between traditional and LLMs in medical education.
| Aspect | Traditional Medical Education Resources | LLMs in Medical Education |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility in pacing and content delivery | Adaptive learning experiences tailored to individual learning needs and preferences |
| Interactivity | Passive learning experiences such as lectures and textbooks | Interactive learning experiences with real-time feedback and explanations |
| Personalization | Generic learning materials not tailored to individual learning objectives | Personalized study plans and learning materials customized to specific learning goals |
| Accessibility | Access to resources may be limited by availability, cost, or location | Accessible anytime, anywhere, with internet connectivity |
| Engagement | Limited engagement with static learning materials | Engaging and interactive learning experiences with simulations, case studies, and multimedia content |
| Feedback | Limited opportunities for real-time feedback and clarification | Immediate feedback and explanations on concepts, terminology, and clinical scenarios |
| Application to Practice | Limited opportunities for application and practice of clinical skills | Realistic simulations and case studies that allow for the application of knowledge in clinical practice |
| Scalability | Limited scalability of traditional methods, especially in resource-limited settings | Scalable and accessible to a wide range of learners, regardless of geographic location or resource availability |
LLMs serve as powerful tools in medical education, offering dynamic and personalized learning experiences tailored to individual needs. These models excel at elucidating complex medical concepts, breaking down information into digestible formats, and providing interactive visualizations and simulations. Additionally, LLMs simulate patient interactions, enabling professionals to practice communication skills and clinical decision-making in a virtual environment.
Simulating patient encounters, LLMs offer instant clarifications on medical concepts and terminology, bolstering understanding and confidence in clinical practice. They provide feedback on diagnostic tests, treatment plans, and therapeutic interventions, enhancing clinical reasoning and problem-solving skills. Overall, interactive learning with LLMs surpasses traditional methods, enriching the educational journey and advancing the quality of education.
Enhancing Accessibility and Comprehension
In traditional medical education, accessibility to learning resources can be a significant challenge, particularly for individuals in resource-limited settings or those with specific learning preferences or disabilities. However, with the advent of LLMs and generative AI, there are several avenues through which accessibility to medical knowledge can be enhanced, thereby facilitating better comprehension and learning outcomes.
- Language Accessibility:
- Traditional medical education resources are often limited to English, posing barriers for non-English proficient learners.
- LLMs offer translation services and generate content in multiple languages, improving access to medical knowledge globally.
- Tailored Learning Materials:
- Traditional resources may not cater to diverse learning needs, leading to comprehension gaps.
- LLMs provide personalized study plans and materials tailored to individual learning objectives and preferences, enhancing comprehension.
- Accessible Formats:
- Traditional textbooks may be challenging for those with disabilities due to dense text formats.
- LLMs transform medical knowledge into accessible formats like audio recordings or simplified text summaries, aiding comprehension for individuals with disabilities.
- Interactive Learning Experiences:
- Passive learning methods may not engage learners effectively.
- LLMs offer interactive experiences such as simulations and quizzes, fostering deeper understanding and retention of medical knowledge.
- Remote Learning Opportunities:
- Traditional education often requires physical attendance, limiting access for remote learners.
- LLMs facilitate remote learning by providing online access to educational content, and overcoming geographical barriers.
Potential LLM use cases in the real world
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the integration of LLMs and generative AI tools into medical education, with several notable case studies highlighting their effectiveness in enhancing learning experiences and improving educational outcomes for professionals at various stages of their careers. These case studies provide valuable insights into the practical applications of LLMs in education and shed light on their potential to revolutionize how medical knowledge is taught and learned.
- Virtual Patient Simulations:
- LLMs enable the creation of virtual patient simulations, allowing medical students to practice clinical scenarios and develop critical thinking skills in a risk-free environment.
- Empirical evidence from studies has highlighted the effectiveness of LLM-based simulations in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and clinical reasoning abilities among medical students.
- Personalized Study Plans:
- LLMs can generate personalized study plans tailored to individual learning objectives, preferences, and pace, optimizing learning experiences and knowledge retention.
- Research findings suggest that adaptive learning platforms powered by LLMs lead to heightened levels of knowledge acquisition and retention among medical learners.
- Interactive Educational Resources:
- LLMs serve as interactive resources, offering instant clarifications, elucidating complex concepts, and providing real-time feedback to enhance engagement and understanding.
- Studies have shown that LLM-powered chatbots contribute to increased engagement and satisfaction among medical students compared to conventional learning methodologies.
These examples use cases demonstrate the diverse applications of LLMs in medical education and highlight their potential to transform the way knowledge is disseminated and acquired. By providing immersive virtual patient simulations, personalized study plans, and interactive educational resources, LLMs empower medical professionals to enhance their clinical skills, deepen their understanding of complex concepts, and ultimately improve patient care outcomes.
Ethical Considerations and Accuracy
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of information provided by AI tools, particularly in healthcare, is of paramount importance due to the potential impact on patient care outcomes and the ethical responsibilities of healthcare professionals.
- Patient Safety and Care Quality:
- Accuracy and reliability are paramount in healthcare, and crucial for patient safety and quality care. Inaccurate AI information known as hallucinations can result in misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatments, impacting patient outcomes. Healthcare professionals depend on precise clinical data to make informed decisions and deliver optimal care. It’s worth noting that most LLMs, including ChatGPT, have exhibited a degree of hallucinations, estimated at a rate of 15% to 20% according to studies.
- Trust and Confidence:
- Trust in AI-driven healthcare technologies is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. Consistent accuracy from reliable AI tools builds trust and encourages their adoption in clinical practice. Conversely, errors in AI-generated content can erode trust and confidence in these technologies, impeding their acceptance and use in healthcare settings..
- Ethical Imperatives:
- In healthcare, AI technologies must meet rigorous standards of accuracy and reliability to uphold ethical principles. Ensuring patient well-being and avoiding harm requires trustworthy AI tools with clinically validated information. Ethical guidelines and regulations emphasize the importance of accuracy and reliability to protect patients and maintain professional integrity.
Studies have evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of AI models compared to human experts in various medical specialties. For example, a study published in JAMA Oncology compared the performance of an AI model to human pathologists in interpreting breast cancer biopsy slides. The AI model demonstrated a lesion-level, true-positive fraction of 72.4% (95% CI, 64.3%-80.4%), indicating its comparable accuracy to human pathologists in detecting breast cancer metastases, highlighting its potential as a diagnostic aid in pathology practice.
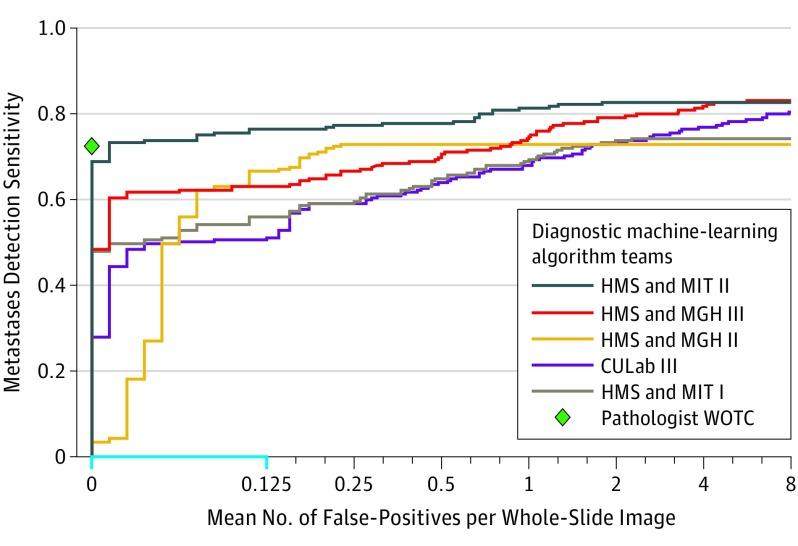
FROC Curves of the Top 5 Performing Algorithms vs Pathologist WOTC for the Metastases Identification Task
In conclusion, the incorporation of large language models (LLMs) and generative AI tools into medical education represents a transformative shift towards interactive, personalized learning experiences. While LLMs offer promising opportunities to enhance comprehension and accessibility of medical knowledge, ensuring their accuracy and reliability remains a critical consideration. Collaboration among educators, developers, and researchers is key to realizing the full potential of LLMs in advancing medical education and improving healthcare outcomes.
